About a million possible cases of atrial fibrillation, a known risk for stroke, go undetected in Japan. A local startup is introducing an innovative AI targeting this growing danger.
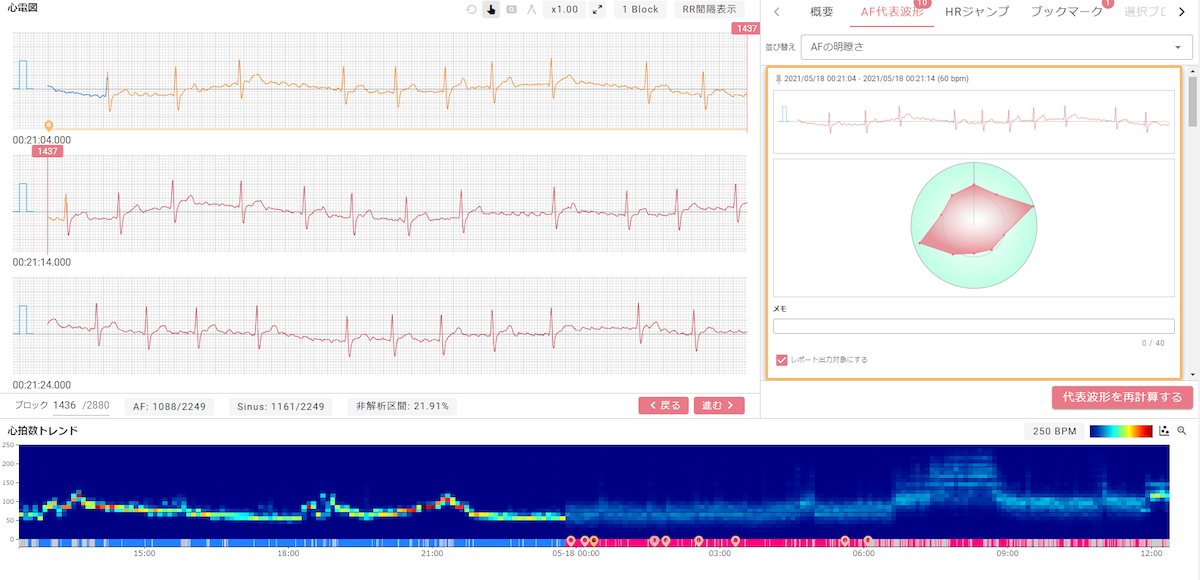
Founded in 2019, Cardio Intelligence develops a range of AI-powered solutions for continuous heart monitoring called SmartRobin AI.
The SmartRobin AI series is based on “explainable AI,” which processes a huge volume of information – an ECG dataset of over 100 million heartbeats – to provide clinicians with simple insights supporting their diagnosis.
The company claims its AI can produce instant analysis of 24-hour ECG in about three minutes and 7-day ECG in around 15 minutes.
The AI lineup currently covers both continuous ECG tracking and AFib detection.
Mobihealth News spoke with Yuichi Tamura, CEO of Cardio Intelligence, who discussed more about their latest work in detecting AFib and how they are helping Japan shed light on this silent threat.
Q. You are currently developing a new AI to detect AFib. Where are you now in this process and what can you tell us about this technology and the problem it seeks to solve?
A. We have already obtained medical device approval for the AI system for detecting AFib, and it is currently being sold in Japan. Our technology leverages deep learning algorithms to quickly analyse vast amounts of ECG data collected over seven to 14 days. The primary challenge we are addressing is improving the diagnosis rate of paroxysmal AFib, which often presents no symptoms but can lead to serious complications like stroke if left untreated. By providing clinicians with a reliable early detection tool that minimises the burden on medical staff, we aim to improve patient outcomes and reduce healthcare costs associated with advanced cardiovascular diseases.
Q. Can you share the details of your study findings after testing your AFib AI detection model?
A. When detecting AFib from standard long-term ECGs, our AI model demonstrated a sensitivity of 97% and a specificity of 95%. This research was published prior to our product launch. Recently, we have been conducting clinical studies in collaboration with several leading hospitals in Japan. The positive rate of AFib [detection adoption] has reached 15%, indicating that our AI model is being effectively utilised. We are also working on integrating physician feedback to improve result interpretability and enhancing the user interface to make the system even more user-friendly.
Q. There are many ECG analysis AI solutions currently in the market. How do you set your product suite apart from them? What is your product development strategy and what unique value do your AI products propose?
A. Our software medical device products are compatible with any existing ECG hardware. Each product features an interface that is easy for physicians and technicians to use. Unlike other black-box solutions, our AI-powered software provides explainable results that allow clinicians to understand the reasoning behind each detection.
Our development strategy focuses on solving challenges in clinical settings and maximising efficiency in examinations by collaborating with specialists and healthcare providers – we have already secured such clients to ensure our solutions meet real-world needs.
Q. What are your plans for expansion? Have you looked for or received investments over the past few months/years? Which markets do you intend to bring your ECG analysis AI solutions to?
A. We are actively planning to offer our products outside Japan, particularly in Asia and North America. We have continuously raised funds from strategic investors who share our vision of advancing cardiovascular care through AI technology. We are also exploring partnerships with international healthcare organisations to facilitate our entry into new markets. Our goal is to make our ECG analysis AI solutions available globally, improving cardiac care and patient outcomes worldwide.
_
Yuichi’s responses have been edited for clarity’s sake.